What is the Debt to Equity Ratio?
The debt to equity ratio is a solvency ratio that shows the extent to which a company finances its assets with debt or equity.
How to Calculate the Debt to Equity Ratio
The debt to equity ratio is calculated by dividing total liabilities by total shareholders’ equity. Both are reported on a company’s balance sheet.
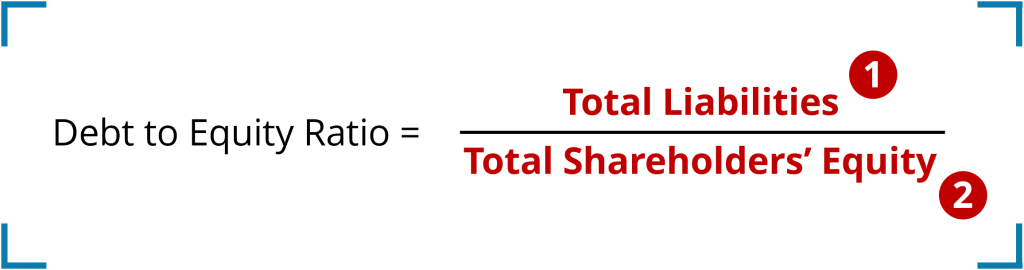
How to Interpret the Debt to Equity Ratio
A low debt to equity ratio means that a company finances its assets primarily with equity, whereas a high debt to equity ratio means that it finances its assets mainly with debt.
The higher the debt levels compared to equity, the higher the chances that a company might run into solvency issues down the road, i.e., it might not be able to make the interest payments and may be forced into bankruptcy.
The following scenarios can be considered:
- No debt: A debt to equity ratio of 0 means that a company has no debt, and is 100% financed with equity.
- Moderate debt: A ratio of 1 means that the assets are financed with equal amounts of debt and equity.
- High debt: A ratio of 4 means that the assets are financed with 4x more debt than equity.
- Extremely high debt: A ratio of 0.99 is an extreme risk scenario where a company finances its assets with 99x more debt than equity.
